5G नेटवर्क: क्या है और यह कैसे चलता है – समझें इस डिजिटल बदलाव को
The Rise of 5G Technology: What to Expect in the Digital Revolution
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the rise of 5G, has become a defining moment in the digital revolution. As we transition from the era of 4G connectivity, the implications of 5G technology are set to reshape the way we live, work, and communicate. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of 5G technology and what to expect as it continues to gain prominence.
5G technology promises ultra-speed, minor latency, and great capacity. It may bring transformational impacts on industries, ranging from smart cities to autonomous vehicles, making our digital lives seamless and effective.
What to Expect from 5G Technology? The answer is, Users are going to get higher internet speed, better reliability of the network, and less latency, hence making real-time applications smoother. This would, in turn, help improve IoT, smart cities, and enhanced mobile experiences; boost innovations across industries such as healthcare, automotive, and entertainment.
5G mobile has been available in the market since the 5G technology has evolved. The 5G mobile, has a faster loading speed than other smartphones. The 5G mobile is available in the market, starting at around, ₹10,000. Samsung Galaxy series 5G mobile is available starting at around, ₹10,000, making the lightning speed of the internet available to the common man.
Jio has made its 5G services available in the last 2 years. With AI evolving by leaps and bounds, 5G technology is going to be a big advantage to AI. 5G wireless service is available in the form of Jio Fibre to speed up the Wi-Fi services.
OTT-App subscription included in ₹999, and ₹1499 plans at 150 Mbps and ₹300 Mbps speeds respectively. You can get all PAID OTT apps at no extra cost. This includes Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney Hotstar, Jio Cinema, Zee5, Sony LIV, Voot, ALT Balaji. Sun NXT, Shemaroo, Lion Gate PLAY, Hoichoi. India is an evolving market for 5G service.

| Aspect | Description | |
|---|---|---|
 | Blazing Fast Speeds | 5G offers significantly higher data transfer rates compared to 4G, enabling faster download/upload speeds, seamless video calls, and immersive online gaming. |
| Low Latency | 5G minimizes latency, crucial for real-time applications like AR, VR, and autonomous vehicles, ensuring quick response times and efficient communication. | |
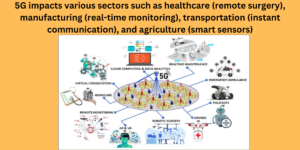 | Revolutionizing Industries | 5G impacts various sectors such as healthcare (remote surgery), manufacturing (real-time monitoring), transportation (instant communication), and agriculture (smart sensors). |
| Challenges and Concerns | Issues include infrastructure deployment, security threats, potential health implications, and the digital divide between urban and rural areas. | |
| Global Implementation | Countries worldwide are racing to adopt 5G technology, aiming for economic competitiveness and technological advancement in the digital age. |
Blazing Fast Speeds:
One of the most anticipated features of 5G is its lightning-fast speeds. Compared to its predecessor, 4G, 5G technology boasts significantly higher data transfer rates. This translates to quicker download and upload speeds, enabling users to stream high-definition content, engage in seamless video calls, and experience immersive online gaming like never before.
How does this happen?
- 1.Frequency Bands and Spectrum Allocation:
- 5G operates on higher frequency bands than 4G. These higher frequencies allow for more data to be transmitted in a given time frame.
- Example: Imagine you’re at a crowded concert. In the 4G era, it’s like having a few wide doors through which people can enter and exit. But with 5G, there are many smaller doors, allowing more people to move in and out simultaneously. These “doors” represent the frequency bands, and 5G’s higher bands enable faster data transfer.
- The available spectrum for 5G is wider, allowing for more simultaneous connections and higher data rates.
- Example: Picture a busy highway with multiple lanes. 4G had a limited number of lanes (frequency bands), causing traffic jams during peak hours (congestion). 5G widens the highway, adding more lanes (higher frequency bands), accommodating more users (simultaneous connections) and allowing faster speeds (higher data rates).
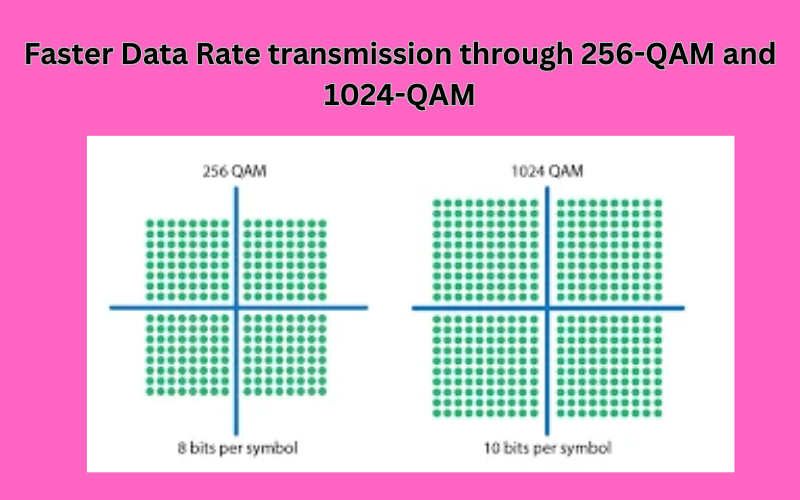
- 2.Modulation Techniques:
- 5G uses advanced modulation techniques (such as 256-QAM and 64-QAM) to encode data more efficiently.
- Example: Suppose you’re sending a high-definition video stream over 5G. 256-QAM allows the transmitter to encode more data per symbol, resulting in faster data rates. However, it’s sensitive to noise and interference.
- These techniques allow more information to be transmitted per radio wave, resulting in higher data rates.
- Example: Imagine a 64-QAM signal carrying voice calls. It can represent 64 different combinations of amplitude and phase, allowing for clear voice transmission.
- 3.Massive MIMO (Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output):
- 5G base stations (cell towers) use massive MIMO technology, which involves multiple antennas.
- Massive MIMO enables better spatial multiplexing, allowing the base station to serve multiple users simultaneously with high data rates.
- Imagine a crowded stadium during a major sports event. The 5G base station (cell tower) equipped with Massive MIMO serves hundreds of users simultaneously.
- Each user’s device communicates with the base station using multiple antennas, allowing for efficient data exchange.
- Whether you’re streaming live video, browsing, or making video calls, Massive MIMO ensures a seamless experience for everyone, even in densely populated areas.
- 4.Beamforming:
- 5G employs beamforming, which focuses the signal directly toward the user’s device.
- This targeted approach improves signal strength and reduces interference, leading to faster speeds.
- Picture a crowded area with many users accessing 5G simultaneously.
- Without beamforming, the base station’s signal would spread out, causing interference and reducing overall speed.
- With beamforming, the base station identifies a specific user (or group of users) and directs a concentrated signal toward them.
- This targeted approach improves signal strength, reduces interference, and leads to faster data rates for those users.

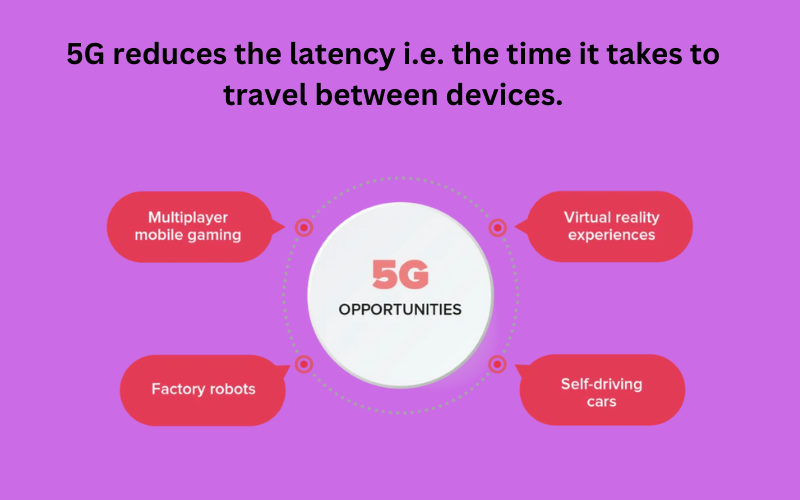
- 5.Lower Latency:
- 5G significantly reduces latency (the time it takes for data to travel between devices).
- Low latency is crucial for real-time applications like video calls and online gaming.
- Video Calls: In a 5G network, video calls have minimal delay. You see and hear the other person almost instantly.
- Online Gaming: Gamers benefit from low latency. Actions like shooting, dodging, or building structures happen without noticeable lag.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on split-second decisions. Low latency ensures timely communication between sensors and control systems.
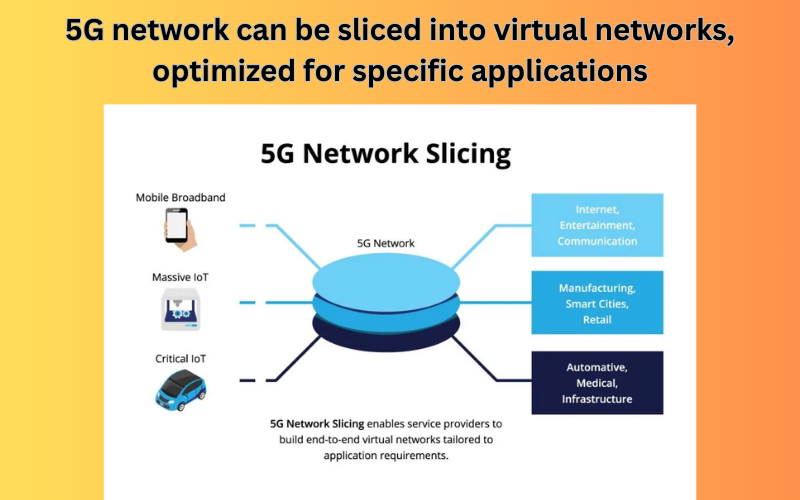
- 6.Network Slicing:
- 5G networks can be sliced into virtual networks optimized for specific use cases.
- For example, a slice can be dedicated to ultra-fast broadband, ensuring high-speed internet for streaming and downloads.
- 7.Edge Computing:
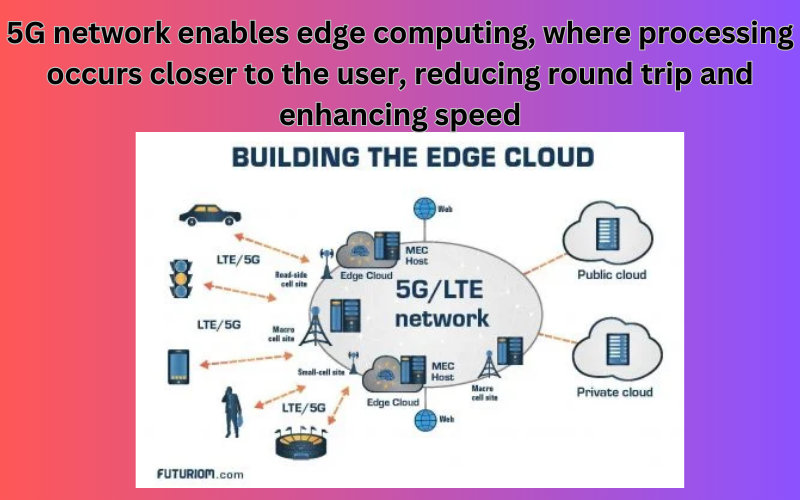
- 5G enables edge computing, where processing occurs closer to the user (at the network edge).
- This reduces the round-trip time for data requests, enhancing overall speed.
Low Latency:
Latency, or the delay between sending and receiving information, is a critical factor in the performance of digital applications. 5G technology is designed to minimize latency to almost negligible levels. This is particularly advantageous for applications that demand real-time responsiveness, such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and autonomous vehicles.
How does this happen?
- Latency, the time delay between sending and receiving information, plays a crucial role in the performance of digital applications. Let’s explore how 5G technology achieves minimal latency levels:
- 1.Network Architecture:
- 5G networks are designed with a more efficient architecture, reducing the time it takes for data to travel.
- Edge computing, where processing occurs closer to the user, helps minimize round-trip delays.
- 2.Faster Transmission Speeds:
- 5G operates at higher frequencies, allowing for faster data transmission.
- This speedier communication contributes to lower latency.
- 3.Small Cell Deployment:
- 5G networks use smaller cells (base stations) distributed more densely.
- Smaller cells reduce the physical distance between devices and base stations, resulting in lower latency.
- 4.Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC):
- 5G introduces URLLC, a mode optimized for ultra-low latency applications.
- URLLC ensures that critical data (e.g., autonomous vehicle control signals) experiences minimal delay.
- 5.Quality of Service (QoS) Prioritization:
- 5G allows network operators to prioritize specific applications.
- Real-time applications like AR, VR, and autonomous vehicles receive higher priority, minimizing latency.
- 6.Predictive Algorithms:
- 5G networks use predictive algorithms to anticipate user behavior.
- By preloading data or optimizing routes, latency is further reduced.
- 7.Slicing and Isolation:
- Network slicing creates virtual networks tailored to specific use cases.
- Slices for real-time applications isolate traffic, ensuring low latency.
Revolutionizing Industries:
Beyond the realm of personal devices, 5G is poised to revolutionize various industries. From healthcare and manufacturing to transportation and agriculture, the high-speed, low-latency capabilities of 5G enable the development of innovative applications. Remote surgery, smart factories, and precision agriculture are just a few examples of how 5G is transforming traditional industries.
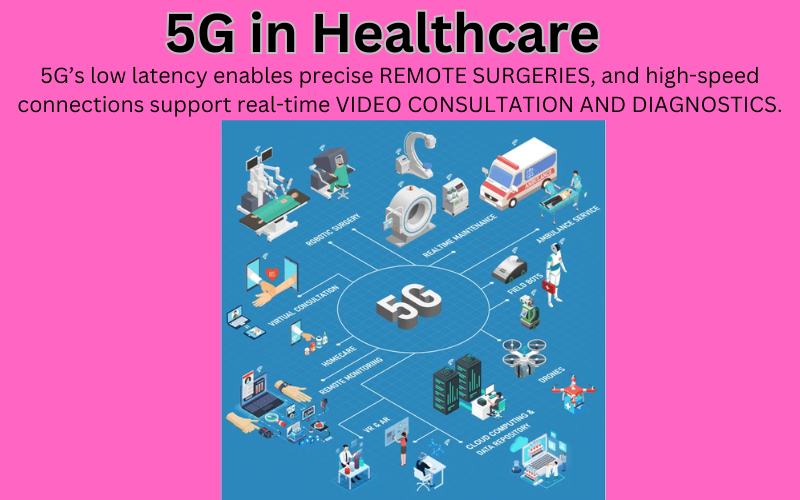
- 1.Healthcare:
- 5G’s low latency allows surgeons to perform procedures remotely with precision.
- High-speed connections enable real-time video consultations and diagnostics.
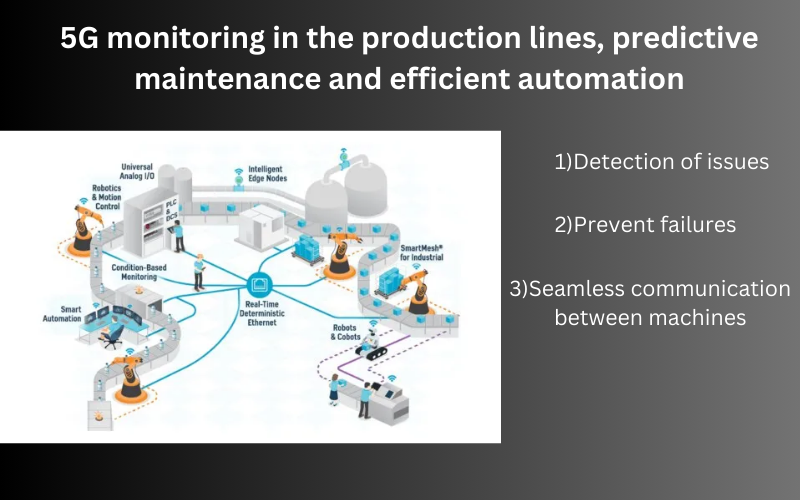
- 2.Manufacturing:
- 5G facilitates real-time monitoring of production lines, predictive maintenance, and efficient automation.
- Connected sensors and devices enhance productivity and safety.
- 3.Transportation:
- 5G enables instant communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and pedestrians.
- Low latency aids in managing traffic flow and reducing congestion.

- 4.Agriculture:
- 5G supports smart sensors, drones, and autonomous machinery for optimized crop management.
- Real-time data helps monitor animal health and behavior.

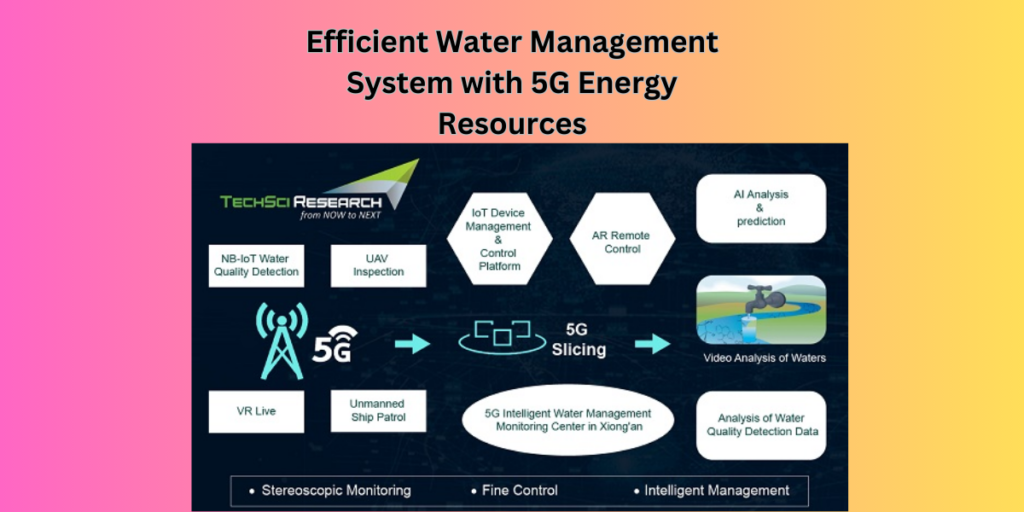
- 5.Energy and Utilities:
- 5G enhances energy distribution efficiency and grid management.
- Real-time monitoring of water supply and quality.
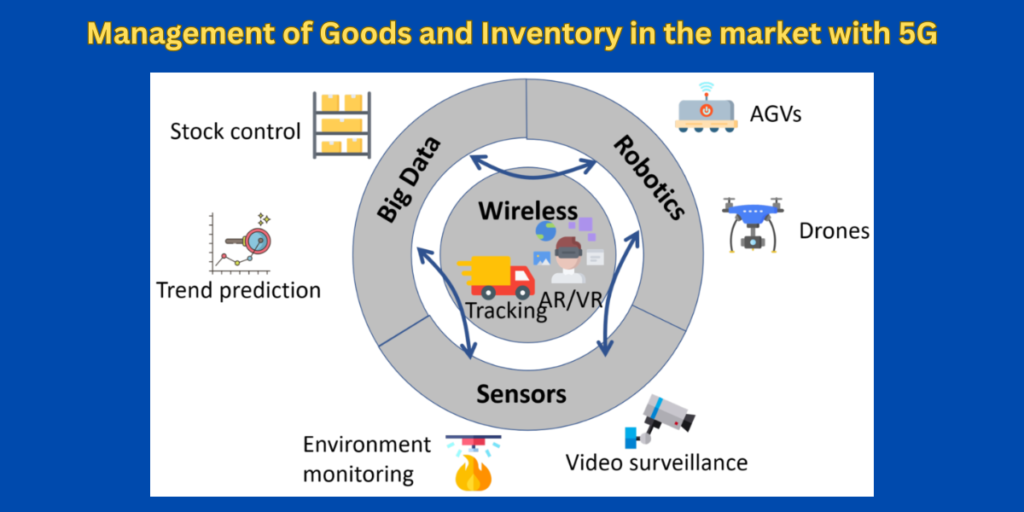
- 6.Retail and Logistics:
- 5G enables accurate tracking of goods and inventory.
- Low latency enhances AR experiences for customers.
- 7.Entertainment and Media:
- 5G powers AR/VR (Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality) content, interactive gaming, and live streaming.
- Faster speeds allow seamless content delivery.

Let’s explore an example that highlights the benefits of 5G technology in the field of healthcare:
Scenario: Remote Surgery with 5G
In a bustling urban hospital, Dr. Maya, a skilled surgeon, receives an urgent call. A patient in a rural clinic requires immediate surgery, but there’s no specialist available on-site. The patient’s condition is critical, and time is of the essence.
Low Latency and Precision:
- Dr. Maya dons her surgical gear and enters the operating room. The patient lies on the table, prepped for gallbladder removal.
- Thanks to 5G’s ultra-low latency, Dr. Maya can control robotic surgical instruments remotely. Her movements are precise and instantaneous.
- As she manipulates the robotic arms, the delay is imperceptible. The patient’s safety relies on this responsiveness.
High-Speed Connections for Real-Time Consultations:
- Dr. Patel, an expert in gallbladder surgery, is miles away at another hospital. He joins the surgery virtually via a high-definition video link powered by 5G.
- Dr. Patel observes the procedure in real time. He provides guidance, shares insights, and ensures that Dr. Maya follows best practices.
- The seamless video connection allows Dr. Patel to see every incision, suture, and tissue manipulation as if he were in the same room.
Diagnostics and Decision-Making:
- During surgery, unexpected complications arise. The patient’s gallbladder is more inflamed than anticipated.
- Dr. Maya consults with Dr. Patel via the 5G video link. They discuss alternative approaches, weigh risks, and make informed decisions.
- Together, they adjust the surgical plan, ensuring the best outcome for the patient.
Patient Recovery and Follow-Up:
- Post-surgery, Dr. Maya monitors the patient’s progress remotely. Vital signs, wound healing, and recovery are tracked using connected devices.
- The patient receives personalized instructions via video consultations. Dr. Maya ensures proper care without requiring the patient to travel.
In this scenario, 5G technology enables precision, real-time collaboration, and life-saving interventions. Surgeons like Dr. Maya can extend their expertise beyond geographical boundaries, bridging th
Challenges and Concerns:
While the promises of 5G are substantial, there are also challenges and concerns that need to be addressed. Issues such as infrastructure deployment, security concerns, and potential health implications have been subjects of debate. It’s essential for stakeholders to work collaboratively to ensure a smooth and responsible rollout of 5G technology.
- Network Security:
- 5G networks, like their predecessors, are susceptible to security threats. However, the risks are amplified due to the sheer volume of connected devices and the sensitive data they handle.
- Cybersecurity concerns range from data privacy and protection to potential threats to critical infrastructure.
- The decentralized nature of 5G networks, with more data being processed at the edge, introduces new points of vulnerability.
- Telecom operators and device manufacturers must invest significantly in robust security measures to safeguard against these threats.
- Cost of Infrastructure Development:
- Transitioning from 4G to 5G requires a complete overhaul of existing infrastructure.
- This includes deploying new antennas, base stations, and high-speed fiber connections.
- The substantial cost of infrastructure development could be a barrier to 5G rollout, especially in rural and remote areas where the return on investment may be lower.
- Ecosystem Availability:
- The full potential of 5G can only be realized when a comprehensive ecosystem of 5G-enabled devices and applications is available.
- This ecosystem encompasses not only smartphones but also IoT devices, industrial equipment, and autonomous vehicles.
- Currently, the development of this ecosystem is still in its early stages, and it will take time for a wide range of 5G-compatible devices and applications to become available.
- Health Implications:
- While extensive research has not definitively proven adverse health effects from 5G radiation, concerns persist.
- Some worry about increased exposure to electromagnetic fields and potential long-term health consequences.
- Regulatory bodies continue to monitor and assess the impact of 5G on human health.
- Digital Divide Risk:
- The rollout of 5G technology may exacerbate existing disparities in connectivity.
- Urban areas are likely to benefit from 5G sooner, while rural and underserved regions may lag behind.
- Bridging this digital divide requires collaborative efforts among stakeholders to ensure equitable access to 5G networks.
Global Implementation:
The deployment of 5G is a global effort, with countries around the world racing to adopt and implement this transformative technology. The competition to lead in 5G development is not just about technological superiority but also about economic competitiveness in the digital age.
The rise of 5G technology marks a significant milestone in the evolution of our digital landscape. From faster speeds and low latency to transformative impacts on industries, the potential of 5G is vast. As we navigate the challenges and opportunities that come with this technological shift, it’s clear that the era of 5G is set to redefine the way we connect, communicate, and innovate in the years to come. Embracing these changes will undoubtedly pave the way for a more interconnected and digitally advanced future.
The above article is a reference from Tech Bloggers Database: 45 Best 5G Technology Blogs and Websites in 2024.
What is 5G technology?
5G is the fifth generation of mobile network technology, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity compared to previous generations.
How fast is 5G compared to 4G?
5G can provide speeds up to 10 Gbps, significantly faster than 4G, which typically maxes out around 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps under ideal conditions.


