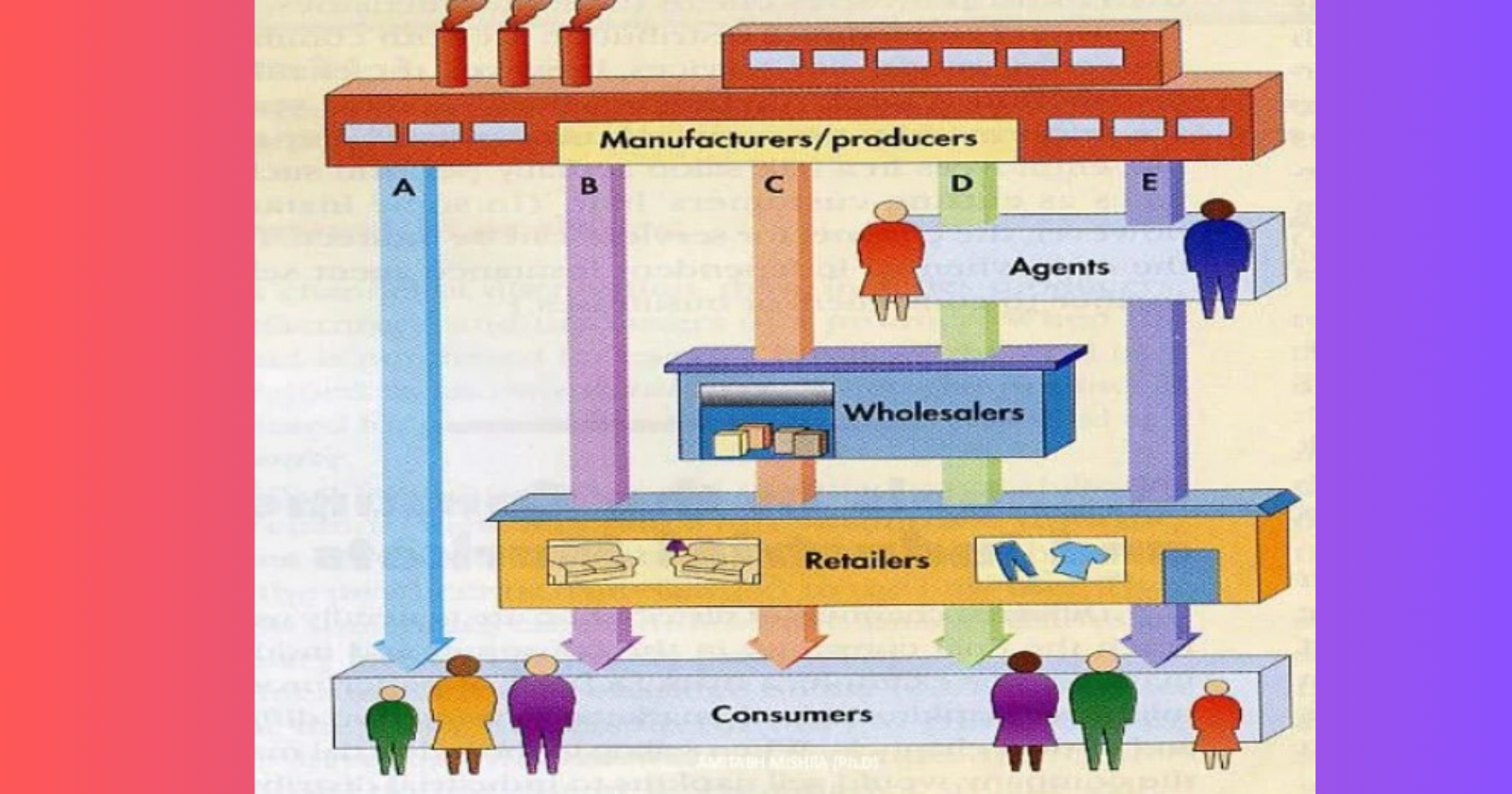
- Distribution is a pivotal element in any business strategy, ensuring products or services reach the right audience at the right time. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of distribution, its significance, and strategies for effective implementation.
- How Can Distribution Be Done Effectively? In this respect, efficient distribution mandates clear logistical efficiency, appropriate supply chain management, and strategic partnerships. It may also involve technologies for tracking inventory levels and routing methods for the most efficient and timely distribution at minimum costs. In other words, any business is largely successful based on how one manages the channels of distribution.
- We are about to uncover the untold story of Starbucks and explore the ground breaking concepts that has the potential to revolutuionize any business distribution channel management.
| Key Aspect | Effective Strategies | |
|---|---|---|
 | Selection of Channel | Choose the right distribution channels based on the target audience and type of product. |
 | Inventory Management | Optimize stock levels to prevent overstocking or stockouts. |
| Logistics Optimization | Lean transportation, warehousing, and delivery processes. | |
 | Technology Integration | Data analytics, automation, and real-time tracking drive efficiency. |
| Collaboration | The smooth running of operations requires the supplier, distributor, and retailer to collaborate. |
Understanding Starbucks Secret secret sauce
- Starbucks in an epitome of a coffee time hovers the secret sauce of aroma of a fresh coffee. The essence of their success lies not just on the coffee, but a strategic focus on distribution and real estate.
- While coffee serves as their product, their main business is expanding their business distribution channel from familiar and fast digital stores encompassing social media to Youtube.
- The Strategic approach isn’t unique to Starbucks, learning and applying from corporate giants like McDonalds and and Walmart and recognize that their heart of the business is from distribution Channels.
- Without a robust distribution channel and effective business there is no sustainable business. It is a transformation of paradiseship that reshapes our understanding of business strategy.

I. Introduction
A. Definition of Distribution
- Distribution, in the business context, refers to the process of making goods or services available to consumers. It involves a series of interconnected activities aimed at delivering products from manufacturers to end-users efficiently.
B. Importance of Effective Distribution
- The success of a business often hinges on how effectively it manages its distribution channels. Efficient distribution ensures that products are available where and when consumers need them, contributing significantly to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Example:
- Imagine a scenario where a company manufactures top-quality products but fails to get them into the hands of consumers efficiently. In this case, the exceptional features and benefits of the products might go unnoticed, leading to missed opportunities for sales and growth.
- When distribution channels are managed seamlessly, products reach the intended destinations promptly.
- Customers appreciate businesses that not only provide high-quality products but also ensure their availability when needed.
- This availability fosters trust and loyalty, creating a positive feedback loop for the business.
- Think about it from a consumer’s perspective – if you consistently find your preferred products on the shelves or online platforms exactly when you want to purchase them, you’re more likely to stick with that brand.
- This reliability builds a strong bond between the business and its customers, establishing a foundation for long-term relationships.
- Furthermore, effective distribution is not just about meeting current demand but also anticipating and adapting to future needs.
- Businesses that can predict market trends and adjust their distribution strategies accordingly stay ahead of the competition.
- Example Reliance Jio, Telecom company established in 2007, Ahmedabad. There was a need for faster internet facilities in India.
- To be ahead of Competitors, like Tata Indicom, Vodafone, Airtel, Idea, Birlasoft.
II. Understanding Distribution
A. What is Distribution?
- Distribution encompasses a range of activities, including transportation, storage, and delivery, all geared towards getting products into the hands of consumers. It’s a critical link in the supply chain that directly impacts a company’s market reach and profitability.
- Lets Understand Distribution though a Case Study.
- Cristina has the business of selling books, however we are guiding her from a product centred approach to a Distributed approach.
- Cristina could serve book on amazon for $9.95 with a straightforward approach to a 70% profit margin. However this model proposes a significant channel, approaches challenges. She has no access to customer information. The approach remains on constant book sales and focusses on luminous process of advertising. Unfortunately this is a common trap that many entrepreneurs fall into.
Building the distribution channel
- It involves a more strategic and a more sustainable approach. This is a art of building a distribution channel. Cristina shares information with interested people by connecting with them through regular emails containing useful content. She uses an email list as the distribution channel, providing valuable content in a free email newsletter.
- Cristina not only builds a relation letter but also creates a reservoir of goodwill. Overtime Cristina becomes a trusted authority of her niche. Each email subscriber becomes a useful asset with an estimated work of around $1 per month. Imagine the potential that Cristina has about 5000 readers potentially $5000 per month.
- The probablility expand exponentially to 20000 readers with $20000 per month. It is about the goodwill of Cristina that keeps the distribution channels engaging consistently.
Monetizing the Distribution Channel
- How does Cristina convert this revenue into Strategic promotion and services that genuinely benefit our readers. The value of each subscriber’s to passage the initial estimation of $1 per month. Cristina transforms business into revenue generating powerhouse. With the right strategy, Cristina can actively market her book on platforms like Facebook, rapidly increasing her list growth.
- In the next 12 months her vision having her around 100,000 subscribers resulting in $100,000 per month.
Leveraging Affiliate Marketing
- The journey doesn’t end there. Cristina can leverage products and services created by others. By becoming affiliate she earns commissions foe every sales. By transforming 50% commission of 50% product and $25 in her pocket.
- However there are two golden rules in Affiliate Marketing. Only promote products that have better quality and have benefited their audiences. Its about monitoring gains, its about maintaining trust and good will over her distribution channel.
B. Role of Distributors and Distribution
- Distributors play a crucial role in the distribution process. They act as intermediaries between manufacturers and retailers, ensuring a smooth flow of goods through the supply chain. Effective distribution through reliable distributors enhances market penetration.
Following the above example: Approximately 1100+ Jio Centers established in India. There are 2 Types of distributors Reliance Jio is offering.
1.ARD
ARD stands for Additional Revenue Generation Device, which is a device or solution that generates additional revenue for Jio Reliance Independence Communication in the form of intercepted and extrapolated commercial data(For SIM activation and Recharge)
2.RDS
RDS, on the other hand, comes from Sensors, IoT, and Monitors, which refers to a group of devices that work together to collect and analyze data from various sources. They can include smart sensors, IoT devices, and monitoring systems, and their data is used to identify patterns and trends that can be used to generate additional revenue for Jio Rel(For hardware like handset and wifi devices)
- Jio a leading Indian Telecommunication Company, has forged partnerships with several smartphone manufacturers like Samsung, LG and Panasonic ecommerce platforms, Flipkart and Amazon India.
Continuous Innovation
- Jio has consistently introduced innovative services and features, strategies ahead of industry trends, launching newspapers, Integrating with Technologies like VoLTE, Jio Fiber establishment, 5G services.
C. Customer-Centric Approach:
- Jio’s success is also attributed to its customer-centric approach. By offering excellent customer service and actively seeking feedback, Jio not only retained its existing customer base but also attracted new customers, further solidifying its market position.
III. Managing Distribution
A. Strategies for Effective Distribution
Implementing successful distribution strategies involves careful planning. From choosing the right distribution channels to optimizing inventory management, businesses must employ a mix of strategies tailored to their specific industry and target audience.
Example: Coca-Cola’s ‘Share a Coke’ campaign encourages consumers to share personalized Coke cans with their friends and family. The campaign was launched in India in 2013, and since then, it has become one of Coca-Cola’s most successful global campaigns. Through this campaign, customers can personalize their own Coke cans with their name or a special message, which can then be shared with others. The campaign has helped to increase brand awareness and generate positive buzz for Coca-Cola in India.

B. Overall Average Revenue in India through Distribution Channels
The average overall revenue in India through distribution channels is constantly changing due to various factors such as market demand, competition, and economic conditions. To obtain the most up-to-date information, it would be best to consult with industry experts or perform market research. As of the most recent data available, the average overall revenue for distribution channels in India was reported to be approximately $100 billion. However, it is important to note that revenue figures can vary considerably depending on the specific company or industry in question.
IV. Growing Distribution Globally
A. Global Distribution Challenges
- Truck loading delays can disrupt delivery schedules and impact operational efficiency.
- Efficient warehouse management involves meticulous searching and staging of goods.
- Providing proof of delivery is a critical component of successful logistics.
- Regular stocktaking is indispensable for effective inventory management.
- To prevent stockouts, businesses must establish robust reordering strategies.
- Efficient handling of returned goods is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and minimizing disruptions.
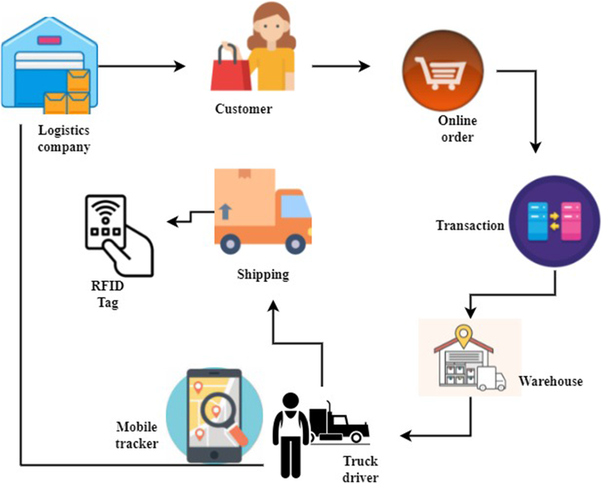
B. Example of High Income Generating Distributors in India
- Redington India Limited,
- Ingram Micro India,
- Supertron Electronics Pvt. Ltd,
- S. P. Richards Company India Pvt. Ltd,
- ITC Distributors,
- Metro Cash & Carry India.
How many behavioral, emotional, cognitive factors, that impact our decision-making, has academic research unearthed so far?
C. Types of Distributors In India
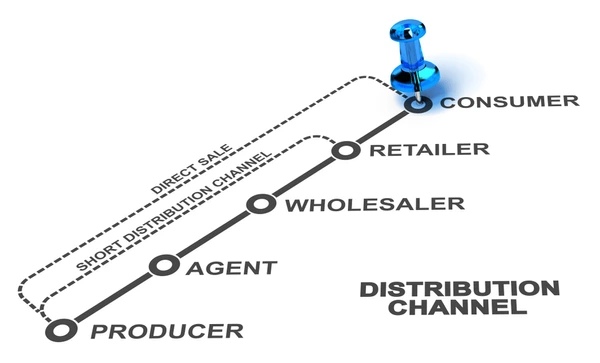
In India, there are various types of distributors that play a crucial role in the supply chain of goods and services. These include:
- Wholesalers: Wholesalers purchase products in bulk from manufacturers and then sell them to retailers or other wholesalers.
- Retailers: Retailers purchase products from wholesalers and sell them directly to consumers. They can be brick-and-mortar stores or online retailers.
- Dealers: Dealers purchase products from manufacturers or wholesalers and sell them to consumers or other dealers. They may specialize in a particular product or group of products.
- Exporters: Exporters purchase products from Suppliers