Unlocking the Potential: Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency
In the realm of technology, blockchain has transcended its initial association with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Beyond the world of digital coins, blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force with innovative applications across various industries. Let’s delve into the exciting landscape of “Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency” and explore the groundbreaking applications that are reshaping the future.
Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency: Innovative Applications, Blockchain technology, beyond cryptocurrency, attracts applications in other fields such as supply chain management, healthcare, and digital identity verification. It ensures secure, transparent, decentralized systems in which trust and efficiency increase across industries, from tracking product origin to streamlining legal contracts using smart contracts.
| Aspect | Description | |
|---|---|---|
 | Decentralized Trust | Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network ensuring transparency without a central authority. |
| Immutability and Security | Once a block is added, it cannot be altered, ensuring data integrity and security. | |
 | Smart Contracts | Self-executing contracts written in code, automating and enforcing terms without intermediaries, used in industries like legal and real estate. |
 | Supply Chain Management | Blockchain provides transparency and traceability, reducing fraud and enhancing efficiency. Examples include Walmart and Nestle. |
| Identity Verification | Secure, decentralized identity management, reducing identity theft risk and giving individuals control over their information. | |
| Healthcare Data Management* | Ensures integrity and security of patient records, enabling interoperability and maintaining privacy while improving data sharing and emergency response. | |
 | Cross-Border Payments | Facilitates faster, cost-effective transactions, with stable cryptocurrencies like USDC used for international transfers. |
| Future Innovations | Ongoing advancements in blockchain technology will continue to redefine business, data security, and digital interactions. | |
| Disadvantages | Blockchain has limitations and challenges, including energy consumption and scalability issues. |
A Foundation Beyond Coins: Understanding Blockchain Technology
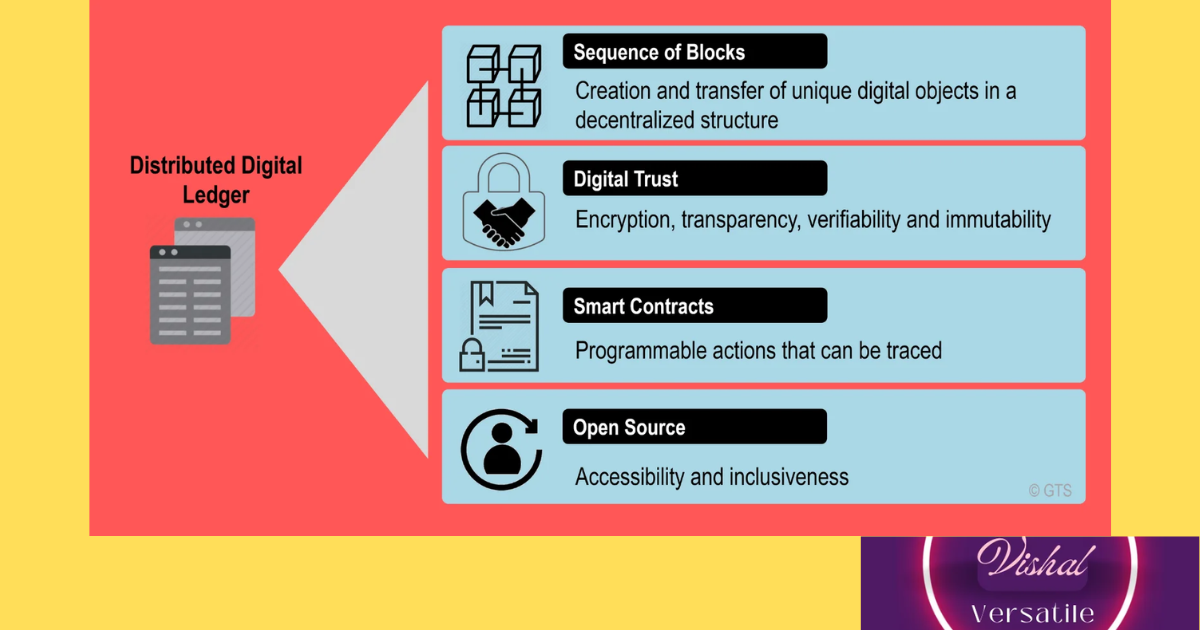
Decentralized Trust: The Core Principle
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology. It operates on a peer-to-peer network, where each participant (node) has access to the entire history of transactions, ensuring transparency and eliminating the need for a central authority.
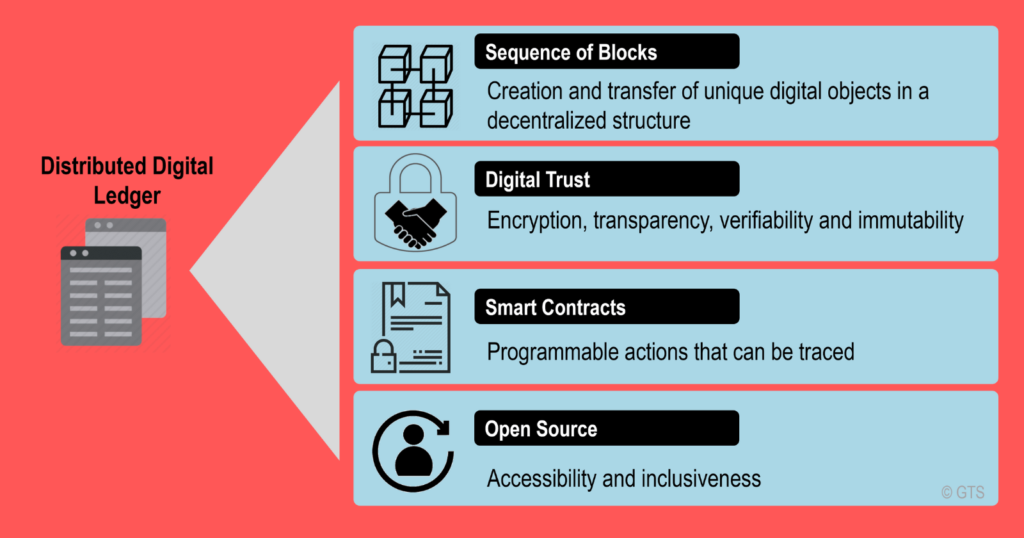
Immutability and Security: Safeguarding Data Integrity
The immutability of blockchain ensures that once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or tampered with. This inherent security feature makes blockchain an ideal solution for applications that require data integrity and resistance to fraud.
Beyond Cryptocurrency: Blockchain’s Diverse Applications
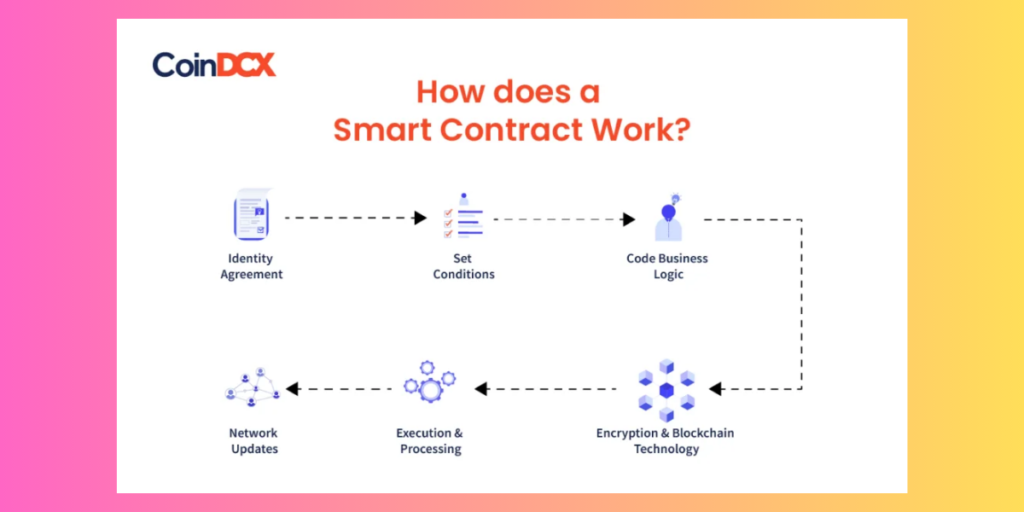
Smart Contracts: Self-Executing Agreements
- Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts run on the blockchain, automating and enforcing the terms without the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts offer efficiency and security that industries from legal to real estate are exploring.
- Imagine it was a digital vending machine, which uses blockchain. Suppose you select the product you want to purchase and enter the correct amount of the product in the machine, the smart contract activates and delivers the chosen product.
- Blockchain Example: Alice wants to sell her house to Bob. They create a smart contract on a BlockChain platform. The contract includes conditions such as the house price, ownership transfer, and payment deadline. Bob who wants to buy the house sends the agreed-upon amount of the house through cryptocurrency to the contract address, the code automatically transfers ownership of the house to Bob. The Bob is unable to pay within the specified time, the contract is automatically canceled and ownership of the house is transferred to Alice. The Most important benefit of the smart contract is that the intermediaries(like lawyers) that were previously required will not be required in this case as the smart contract executes transparency and trust between parties.
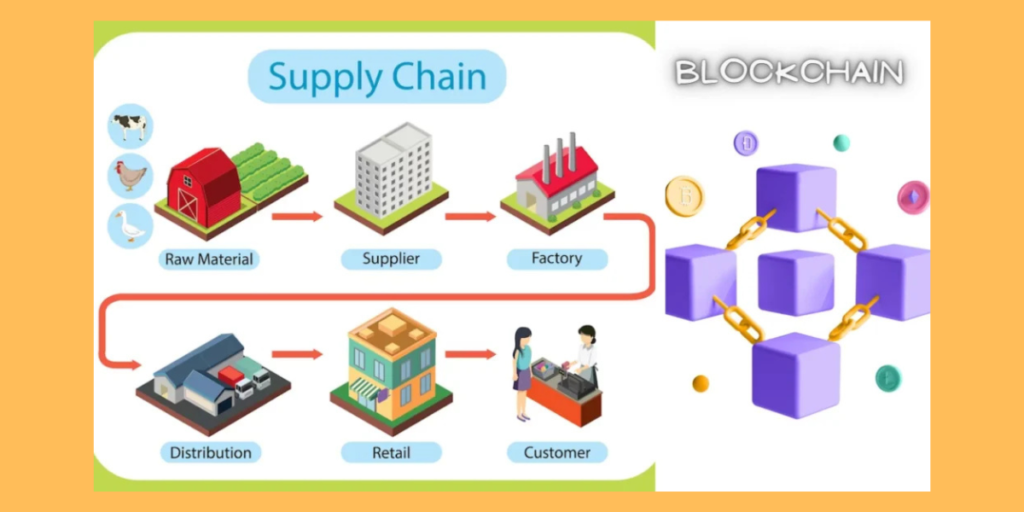
Supply Chain Management: Transparency and Traceability
- Blockchain brings unprecedented transparency to supply chains. With a secure and decentralized ledger, stakeholders can trace the journey of products from manufacturing to delivery, reducing fraud, ensuring quality, and enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
- Blockchain example: Walmart and Nestle execute blockchain in their systems to ensure food safety and security. With the help of blockchains transparency and traceability are secured. Records like origin, quality, and safety of food products is ensured to reduce fraud and consumer trust. Another example, of use of blockchains, is Fed Ex and DHL which ensure real-time tracking of shipments, optimizing routes, and enhancing digital logistics efficiency. British Airways uses blockchains to ensure and verify the data of the passengers and enhance security.
Identity Verification: Strengthening Digital Identity
- Blockchain’s cryptographic features enable secure and decentralized identity verification. This has applications in areas such as digital identity management, reducing the risk of identity theft, and providing individuals with greater control over their personal information.
- Many a times it is required to track the usage of the personal data and securely share it. For this blockchain based identity system enable users to monetize this data.
- Blockchain example: Alice while creating her profile provides verified information such as name age education history on the blockchain platform as a digital identity. Alice specifies certain aspects of her identity she’s willing to share (educational qualifications, work experience) to monetize her data. To access this data, the companies interested directly use cryptocurrency. Whenever a company accesses Alice’s data, a transaction is recorded on the blockchain. Alice can track who accessed her data and for what purpose. Transparency ensures fair compensation and prevents misuse. When applying for a job, Alice shares her verified educational data with the potential employer. The employer instantly verifies the data through the blockchain. No intermediaries or centralized databases are involved.
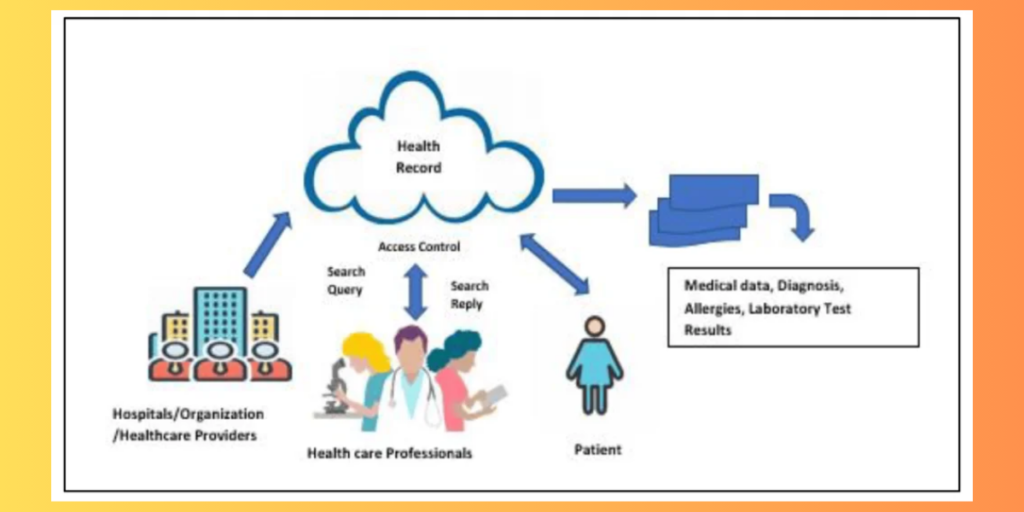
Healthcare Data Management: Enhancing Patient Records
- In healthcare, blockchain ensures the integrity and security of patient records. This decentralized approach enables interoperability between different healthcare systems, streamlining data sharing while maintaining patient privacy and security.
- While managing healthcare data management using blockchain each transaction is recorded in the ledger format.
- Using blockchain it is possible to share, store and access records of patients. The patients can manage and control their own data ensuring privacy over their information. Providing access to specific health providers can achieve this.
- The patients medical history like allergies, treatments and other relevant data, leading to proper decisions and personalized care regarding the patients. specially during emergency situations when any of the patient falls ill, immediate access to patient history can be lifesaving.
- Blockchain example: Imagine a sudden outbreak of a disease in a particular densely populated area takes place. The healthcare systems in those areas use blockchain technology for each patient’s health data(Symptoms, test results, treatment history) to be recorded in blockchain. Each patient’s health is continuously monitored and changes in the medical records are secured. When health experts access the blockchain they can analyze the records of patients, which helps in identifying patterns of the disease, tracking disease spread, and planning interventions. Decision-making becomes easier, Privacy is maintained, and collaborations between different healthcare institutes occur.
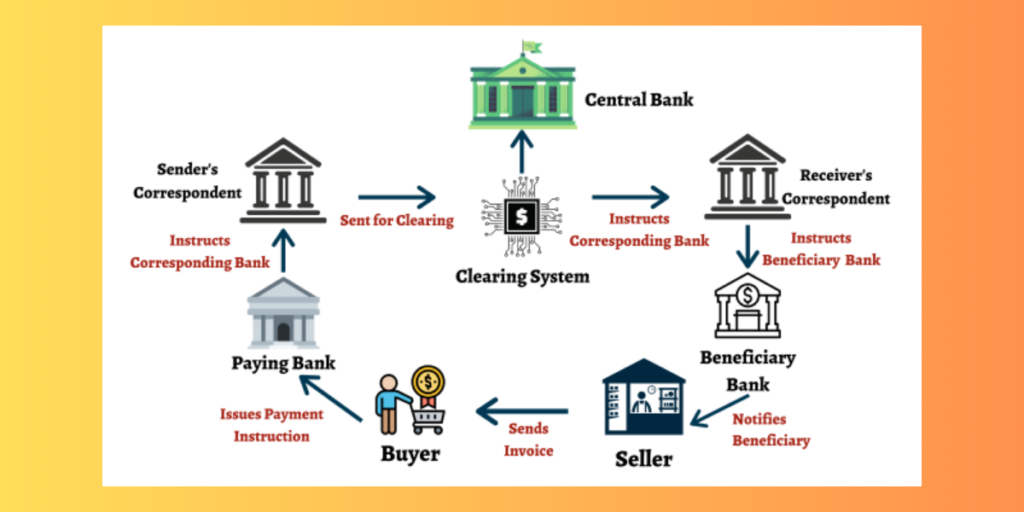
Cross-Border Payments: Simplifying Financial Transactions
- Blockchain facilitates faster and more cost-effective cross-border transactions. Financial institutions and remittance services are exploring blockchain to overcome the challenges associated with traditional payment systems.
- The cryptocurrencies get pegged to stable assets like US dollar. They offer stability and security to cross border payments. USDC(USD Coin is widely adopted for international transactions.
- Financial institutes like Satander and Standard Chartered use cryptocurrencies for cross border payments and to get faster remittances.
Embracing the Future: Innovations on the Horizon
- The journey of blockchain beyond cryptocurrency is an ongoing narrative of innovation and exploration. As industries across the globe recognize the potential of this revolutionary technology, we can anticipate even more creative applications that will redefine the way we conduct business, secure our data, and interact with the digital world.
Exploring the Flip Side: Disadvantages of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain’s journey beyond cryptocurrency is a testament to its versatility and transformative power. From smart contracts to supply chain transparency, blockchain is reshaping industries and ushering in a new era of efficiency, security, and trust. As we navigate this landscape of innovation, the question is not whether blockchain will continue to evolve, but rather, how far its impact will reach. Welcome to the blockchain revolution, where the possibilities are as limitless as the technology itself.
The reference of the above article is,’ IBM. (2019). “Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency.” IBM Think Insights‘.
The ‘blockchainofficial’ is Instagram account which has 109K followers.
Are smart contracts the same as blockchain?
No, smart contracts are self-executing contracts built on blockchain platforms. They automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met.
What are some examples of blockchain platforms beyond Bitcoin and Ethereum?
Hyperledger Fabric: Used for enterprise solutions.
Ripple: Focuses on cross-border payments.
Corda: Designed for business.
Stellar: Aimed at financial transactions.