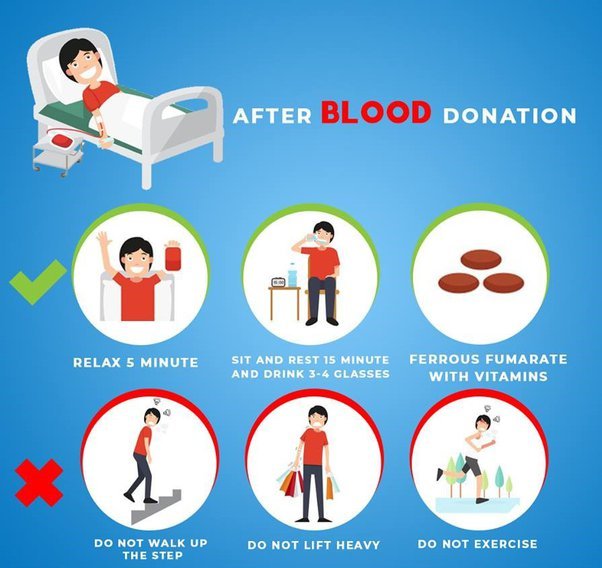
Blood Donation is a generous act with numerous benefits for both the recipient and the donor, but it also has some drawbacks. Here’s an elaboration with examples.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Blood Donation? It is beyond debate that donating blood saves lives, keeps the cardiovascular system healthier, and decreases iron levels in the donor. On the other hand, some might feel dizzy or fatigued for a while afterwards, until they are adequately rested and replenished after such a donation.
| Aspect | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | Saves lives, prevents certain diseases from occurring — like hemochromatosis — and improves mental health. | |
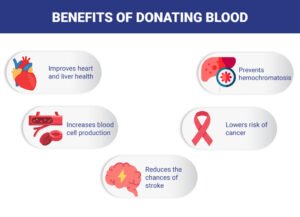 | Health Benefits | Stimulates blood cell production, keeps the heart healthy, and offers a free medical checkup. |
| Disadvantages | Temporary side effects like dizziness, bruising, or feeling tired. Fainting is a rare complication. | |
 | Eligibility Criteria | Must meet health and age requirement; certain medical conditions may disqualify donors. |
Advantages of Blood Donation:
Saving Lives: A single donation can be split into red cells, plasma, and platelets, potentially saving multiple lives. For example, a car crash victim may need red blood cells, a burn victim could require plasma, and a leukemia patient might need platelets.
Here’s how it works:
Whole Blood Donation:
- The donor gives about a pint of whole blood.
- The blood is tested for blood type and infectious diseases.
- Afterward, the blood is separated into its components.
Component Separation:
- A centrifuge is used to break down the donation into red blood cells, plasma, and platelets.
- Each component is collected separately.
- These components are then sent to specific holding areas for further processing and testing.
Usage:
- Red blood cells are often used for car crash victims or patients with anemia.
- Plasma is essential for burn victims and those with clotting disorders.
- Platelets are crucial for leukemia patients and others with low platelet counts.
Health Benefits for Donor: Regular donors can reduce the risk of heart disease and maintain healthy iron levels. For instance, a donor with high iron levels can benefit from the iron reduction that occurs with blood donation, helping to prevent conditions like hemochromatosis.
How it works?
Donating blood helps deplete excess iron in the body. Iron overload has been linked to oxidative stress and atherosclerosis, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Research shows that regular blood donors have an 80-88% lower risk of heart attack compared to non-donors.
Interestingly, this benefit primarily applies to men; female donors show less significant heart health improvement.
By donating blood, men can shed some of their iron stores. This helps prevent cholesterol deposition on artery walls, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
Regular donors tend to have thinner blood, which lowers the risk of thrombosis (blood clotting) and related cardiovascular events.
Free Health Check-up: Donors receive a health screening that can detect issues like high blood pressure. For example, a donor discovers they have hypertension during a routine donation check-up, allowing them to seek treatment sooner.
Research indicates that regular blood donation offers several health benefits, including potential cardiovascular advantages.
Regular blood donors have an 80-88% lower risk of heart attack compared to non-donors.
This benefit is more pronounced in men than in women.
Regular donors tend to have thinner blood, which promotes better blood flow.
Improved blood flow reduces the risk of blood clot formation (thrombosis) and related cardiovascular events.
When donors arrive for blood donation, they undergo a health screening. During this process, their blood pressure is checked to identify any issues, including high blood pressure. If elevated blood pressure is detected, the donor may be advised to seek further medical evaluation.
Psychological Uplift: Donors often feel a sense of accomplishment and joy from helping others. Imagine the pride a donor feels knowing their blood helped a patient recover from surgery.
When donors give blood, they often experience a sense of accomplishment and joy. Knowing that their donation can save lives or improve someone’s health brings a rewarding feeling. It’s a beautiful act of kindness that fosters a positive impact on both the donor and the recipient.
Disadvantages of Blood Donation:
Temporary Discomfort: Donors might feel faint or dizzy after donating. A first-time donor might experience lightheadedness, but this is typically short-lived and can be mitigated by resting and consuming fluids.
Feeling faint or dizzy after donating blood is relatively common. It occurs due to a temporary drop in blood pressure and a reduction in the number of red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body. This phenomenon is known as a vasovagal reaction. The symptoms are usually mild and typically last only for a few minutes or hours.
Iron Deficiency: Regular donation can deplete iron stores, requiring some donors to take supplements. For instance, a frequent donor might need to monitor their iron levels and possibly take iron supplements to maintain good health.
Infection Risk: There’s a small chance of infection at the needle site. For example, a donor might notice redness or swelling at the puncture site, which is usually preventable with proper aftercare.
When donating blood, there’s a small risk of infection at the needle site. Although rare, bacteria could enter through the puncture, leading to localized pain, swelling, and warmth around the donation area. If you suspect an infection, it’s essential to contact the donation center promptly. Rest assured, though, that new, sterile disposable equipment is used for each donor, minimizing the risk of bloodborne infections like HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
While blood donation is largely beneficial and safe, it’s important for donors to be aware of both the advantages and the potential risks involved.

A poem in Hindi on the advantages and disadvantages of Blood donation
रक्तदान के फायदे और नुकसान,
जानो इस विषय में थोड़ी जानकारी।
फायदे (Benefits):
- कैंसर और हेमोक्रोमैटोसिस के खतरे को कम करता है: नियमित रक्तदान से ये खतरे कम होते हैं.
- मोटापे को कम करता है: रक्तदान करने से तनाव कम होता है.
- कार्डियोवैस्कुलर स्वास्थ्य में मदद: यह हृदय स्वास्थ्य को भी सुधारता है.
नुकसान (Side Effects):
- लिवर की क्षति और कैंसर का खतरा: रक्तदान करने से लिवर पर सकारात्मक प्रभाव पड़ता है, लेकिन यह लिवर कैंसर की संभावना कम करता है.
- अत्यधिक लोहे के निर्माण से लोहे की जमावट: रक्तदान से लोहे की जमावट कम होती है, जो खून की गड़बड़ी का कारण बन सकती है.
यदि आप स्वस्थ हैं, तो रक्तदान करने से बचें नहीं, आपके इस सकारात्मक कदम से किसी की जान बच सकती है।
What is the process of blood donation?
The process of blood donation typically involves the following steps:
- Registration: You’ll sign in, show ID, and provide your address.
- Health Screening: You’ll undergo a mini physical exam and answer questions about your health history.
- Donation: A new sterile needle will be inserted into your arm to collect the blood, which takes about 8-10 minutes for whole blood donations.
- Refreshments: After donating, you’ll rest and have a snack and something to drink.
- Recovery: You’ll be monitored for a short period before you can leave and resume normal activities.
It’s important to note that the entire process, from arrival to departure, takes about an hour. Hydrate well before and after donating, and follow any specific instructions provided by the blood donation center.Your contribution is invaluable and can save lives.

Who can donate blood?
Eligibility criteria for blood donation typically include:
- Age: Generally, donors must be between 18 and 60 years old.
- Weight: A minimum weight of 45 kg is required.
- General Health: Donors should be in good health, free from infections, and not experiencing any acute illnesses.
- Hemoglobin Levels: A sufficient level of hemoglobin, usually not lower than 12.5 g/dL, is necessary.
- Medical History: Donors must provide accurate information about their medical history. Certain conditions or medications may temporarily or permanently disqualify someone from donating.
People with certain medical conditions, recent surgeries, or those on specific medications may be deferred from donating. It’s always best to check with a local blood donation center for the most up-to-date eligibility criteria.

How does a person change when he grows old?
How can I find a blood bank near me?
To find a blood bank near you in Maharashtra, you can visit the State Blood Transfusion Council (SBTC) website for Maharashtra, which provides a search feature to locate blood banks and available blood groups in the area.
Refer to the list of blood banks in Mumbai with contact details provided by the Mumbai District AIDS Control Society (MDACS). These resources should help you find a blood bank conveniently located near you. Remember to check the operating hours and whether you need to schedule an appointment before visiting.
Blood donating experiences
- Blood donation is a noble act. In India many adults share their experiences of blood donation in their lives. The nurses prepare the person for blood donation by checking his medical history. The donor lies down on the bed and the non dominant arm is used for blood donation.
- As per the donor’s experience they often feel a sense of fulfillment and pride knowing they’ve helped save lives. It is likely that, some may feel a little dizzy or a feeling of fainting, immediately after blood donation. This is a normal feeling.
- Donors are encouraged to enjoy snacks and hydrate after donating. Mild bruising or soreness at the needle site is common. You have to follow blood donation guidelines provided by the blood center.