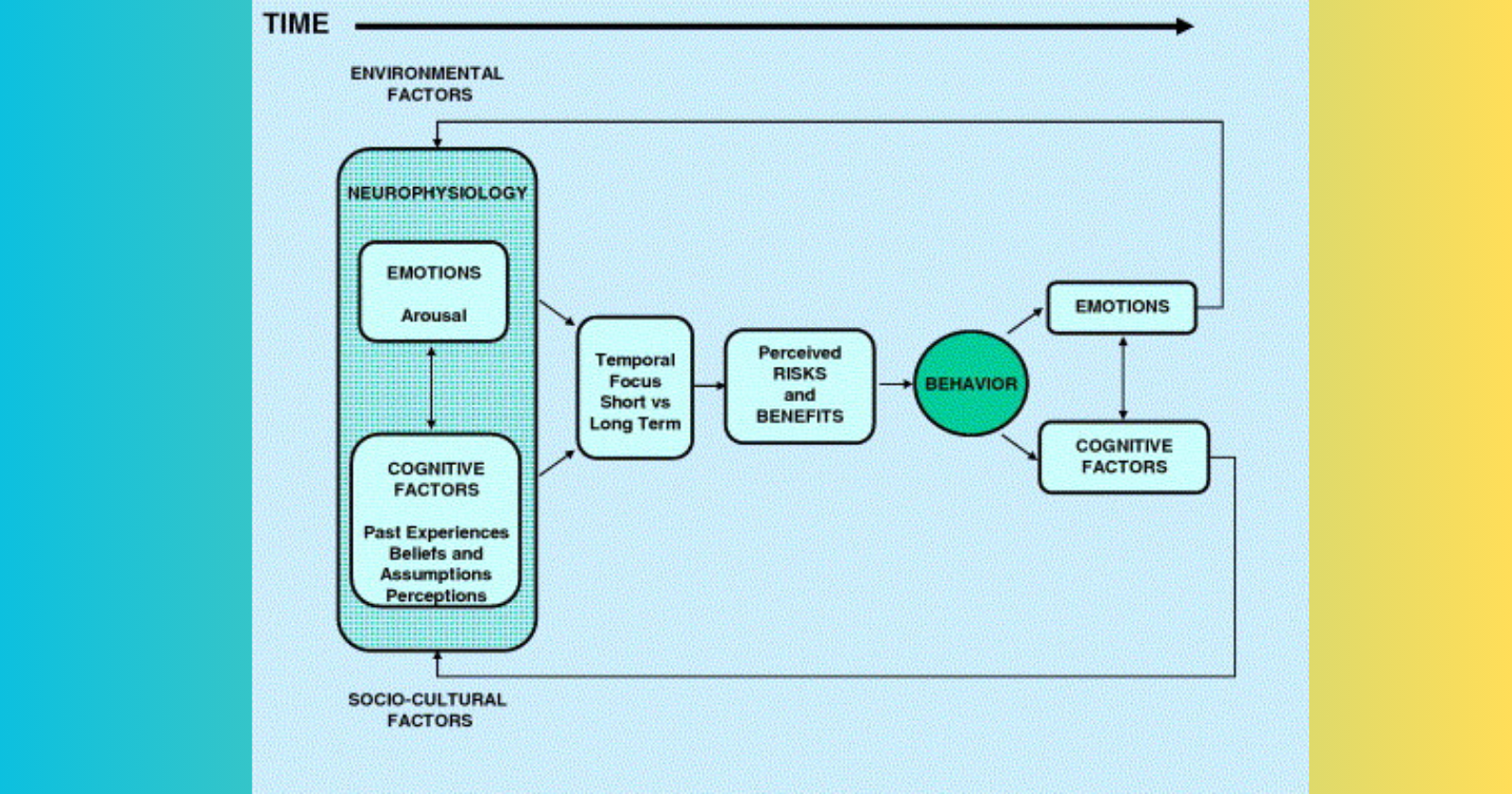
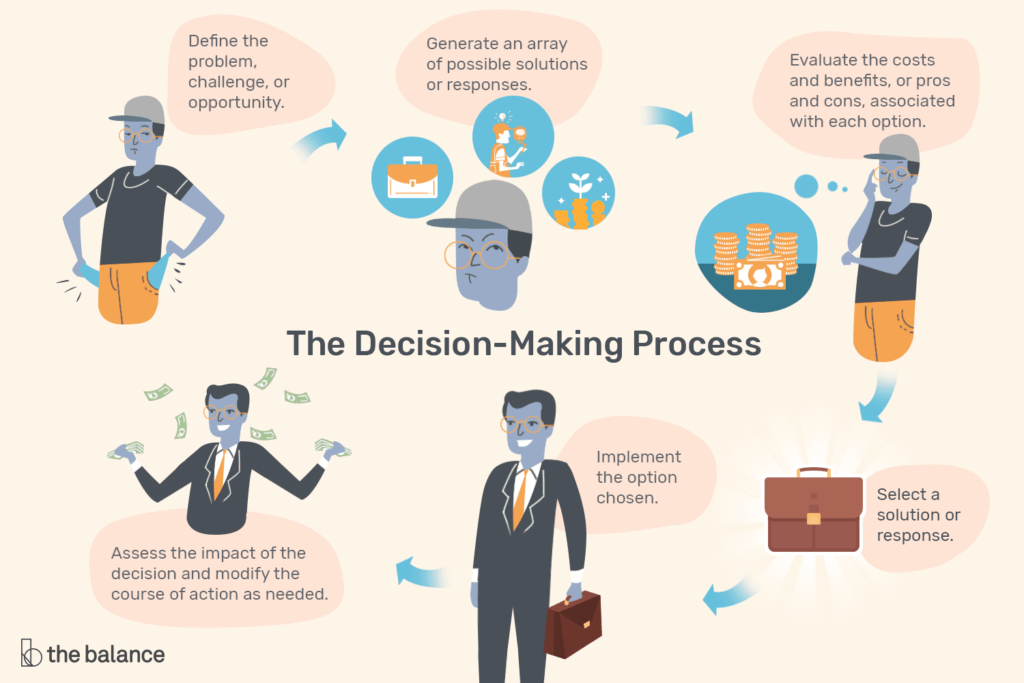
Decision-making is a complex process influenced by an intricate interplay of behavioral, emotional, and cognitive factors. Academic research has delved into the depths of human psychology to unearth the numerous elements that shape the choices we make. In this article, we will explore the extensive array of these factors, shedding light on the wealth of knowledge accumulated through rigorous academic studies.
| Factor Category | Examples of Impacting Factors | |
|---|---|---|
 | Behavioral Factors | Heuristics, biases, habit formation |
 | Emotional Factors | Mood, stress, fear, and emotional regulation. |
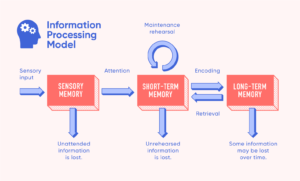 | Cognitive Factors | Information processing, memory, attention, and reasoning abilities. |
| Social Influences | Peer pressure, cultural norms, and social identity. | |
| Environmental Context | Contextual cues, decision environment, and available information. |
How Many Behavioral, Emotional, Cognitive Factors That Impact Our Decision-Making Has Academic Research Unearthed So Far? Research has documented a number of additional factors that affect choice, which strongly include cognitive biases, emotional responses, social influences, and stressors. These are important in understanding human behavior and improving choice.
Understanding Behavioral Factors in Decision-Making
Herd Mentality:
Example of Herd Mentality in Stock Markets:
A classical example of herd mentality is followed in stock markets when the prices of the stocks increase due to positive news. The positive news spreads among the people. These people are influenced by the other people believing in the positive news. So this crowd follows the positive news and invests in the stock. Hence the price of the stock goes up rapidly. This has happened because the investors started buying the stock to earn profits.
There is a fear among the investors that if they follow the positive news and do not invest in the stock, they won’t be able to earn profits. Investors are influenced by the actions of the others who are in majority. The intrinsic value of the stock is analyzed and it is followed by the crowd.
But there is also a disadvantage of the herd behaviour. If there is a certain news, could be positive or negative, if people follow others actions without analyzing the stock there is a possibility that there will be a crash in the market. This is called social influence or financial decision making. To avoid this there should be market analysis by investors, regulators or analysts.
This can make good decision making possible with a collective mentality.

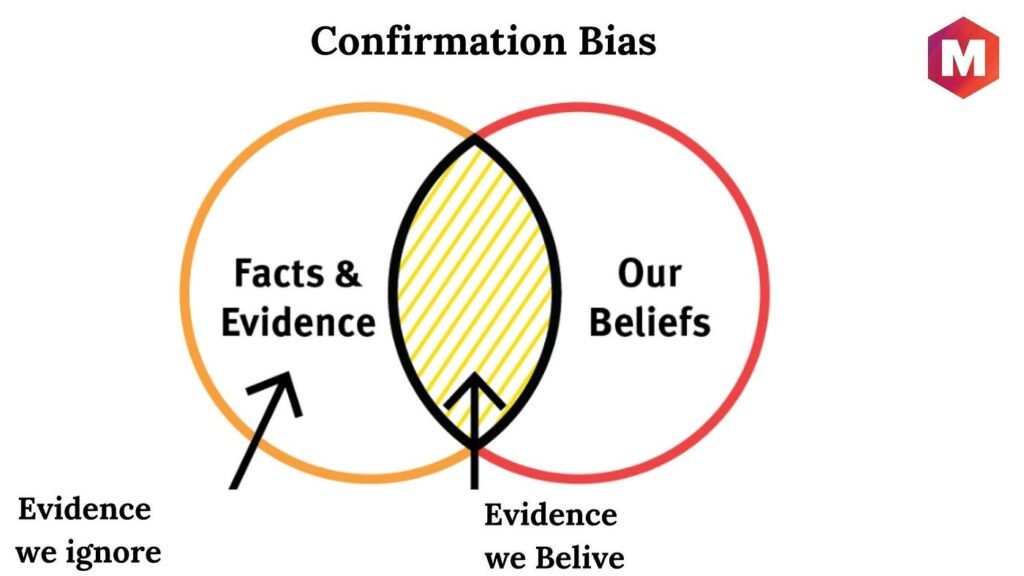
Confirmation Bias:
Example of Confirmation Bias in Political Decision-Making:
Consider an individual who has a strong set of political views and affiliations. These views delve in the mind of the individual because he has been exposed to media platforms on a particular political view and this view has made a permanent house in their mind.
These views and beliefs that they have in their minds are shared by them to their other surrounding people. It may happen that their mind rejects information which is opposite or different from these views and beliefs.
This can happen their minds don’t have the ability to intake information which is different from their views and beliefs stored in their minds. There are scholars and experts in this field of confirmation bias which investigate the mental reasons behind the same old unchanged views and beliefs.
Such people live in a world that agree with their old views and beliefs and like their own ideological beliefs. Recognizing and tackling such confirmative biases in political decision making is crucial for fostering open mindedness and healthy democracy. People should look at the confirmed beliefs to diverse perspectives and questions raised against their beliefs should be addressed. This would solve complex issues.
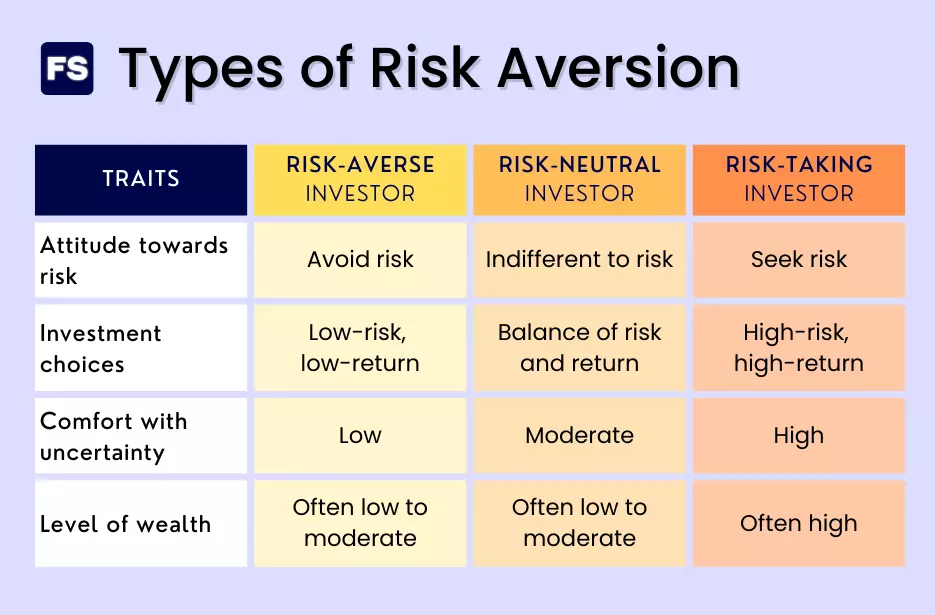
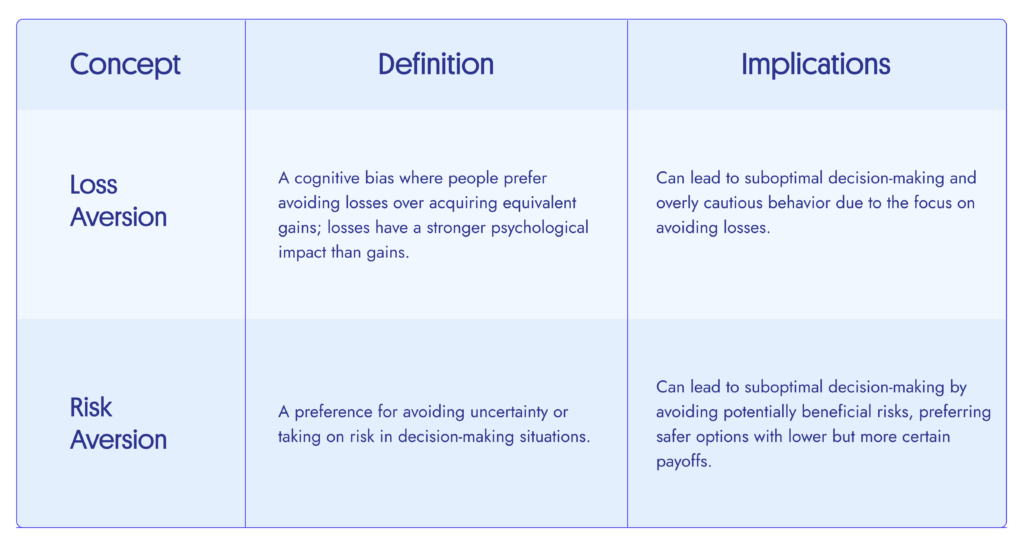
Risk Aversion vs. Risk-Seeking Behavior
Consider two investors, Alex and Jordan, navigating stock market.
Alex is a risk averse as he doesn’t like taking big risks. He prefers less risk. For example, he wants to invest money in anything. It could be government bonds as he prefers more stable form of investment.
Jordan on the other hand is risk seeking behaviour. He prefers to take the risk of investing in volatile stocks and emerging markets. Jordan wants higher rewards so he likely takes big risks of investing in volatile stock. Jordan considers to move out of his comfort zone and his risk has a higher level of uncertainty.
Alex on the other hand prefers to avoid risk and has different attitude towards risk. Since the risk is low in his case, the returns too our low. The level of wealth is Low to Moderate.
In finance realm, it is important to understand the nature of the risks and its risks takers. it helps analysis of the minds, nature and personality of people to perceive risks. Decisions are to be made in the context of the financial investments, strategies to invest with lower and higher risks.
Lower risk involves less money with easy strategies and higher risk involves more money with more complex time consuming strategies.
Anchoring Effect:
Example of the Anchoring Effect in Real Estate Negotiation:
Suppose you want to buy a house and you require negotiating with the real estate agent or the seller about its price. The agent gives a price known as the anchoring price i.e. price on which we can negotiate about buying the house.
The price may be greater or less than the market price of the house, but it remains as a price which remains as a price of reference point. This anchoring price is the arbitrary price suggested by the seller. It becomes a reference point that has a significant effect on the negotiation process.
The buyers find it difficult to deviate from the initial anchor. The anchoring effect is important in negotiations, where the initial offer can set the tone of the entire discussion. It is important to mitigate the anchoring prices and the impact of initial reference points on the decision making process.
Pricing strategies can be carried out on the basis of negotiated values surrounding the anchor prices. This helps make better decisions for facilities that we get from the houses. This analysis and learning from the negotiation process makes the system more efficient.
Unraveling Emotional Influences on Decision-Making
Emotional Intelligence:
This section shows how academic literature plays an important role in managing and recognizing emotions and how it impacts decision making skills. Suppose that there is an employee at a workplace where he receives constant criticism on the project rather than becoming negative about the problem. The approach should be a solution oriented approach.
A person with high emotional intelligence would recognize and manage the emotions in response to the feedback from the opposite side. The reaction would be positive and constuctive, having the awareness about the problem and also one’s capabilities. Instead of reacting defensively or being upset, the emotionally intelligent people ackowledge their feelings. They understand the constructive intent behind the criticism and use it as an opprtunity for growth.
A normal individual who is emotional or has a negative mindset, would become defensive in their working approach and play a safe game at workplace. This is not the case with emotionally intelligent people. for them every failure is an opportunity to learn and grow from it. A regular feedback about performances, leads to the successful execution of the project.
It is important to take suggestions and feedback for every executed successful project, which will make the future projects more efficient and the time required for the completion of the future projects would also be less consumed compared to the already executed ones.
Emotionally intelligent people serve well in their professional and personal lives. It is not only important to get the pros of the growing projects but also their cons. Every aspect is important and also needs to be reflected.
Fear and Anxiety:
Fear and anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness towards a particular risk perception and individual choices. In financial context, suppose that a person has to take a financial decision which involves a risk during a period of economic un stability and uncertainty. in such a situation the person will face high level of fear and anxiety about potential losses that can happen as there involves a particular risk.
Such financial uncertainty changes the thinking of the person about the risk. Mostly what happens is the person leaves just because of fear and anxious state of his mind. This can happen during the period of economic depression or economic unstability in the region. The economic uncertainty can also be about his own financial condition.
Study says that the decision making process is affected by the feeling of anxiety and fear that is experienced by people involved in financial uncertainty.
In a person’s life, his family is his ultimate support system and his financial condition is determined by his financial needs during that period. In such cases the opportunity is left, forgone. Fear and Anxiety affects the financial decision making process. Hence the emotional well being of the head of the family is important who makes financial decisions.
Reward Sensitivity:
Research says that rewards that are expected affects the decision making process, driving individuals toward certain choices. Consider a scenario where an individual has to decide between two jobs. Job A offers higher salary but has high working hours and increased stress, while Job B provides a moderate salary with a better work life balance.
An individual with a high level of reward sensitivity might choose Job A as it affects higher salary reward will empower him with success and prosperity as compared to the Job B with rewards less salary.
The increased financial gain will tempt an individual to choose Job A. There is a study in the field of neuroscience which tells hours brain’s reward system which can drive individuals towards higher immediate gratification or positive outcomes.
This is not only true in the case of an employee but also in the case of an employee but also in the case of self employed businesses or any other individual who wants to earn. Greater efforts are required in the case of individuals who opt for higher rewards in terms of their incomes as compared to those with less rewards.
Loss Aversion:
Emotional reactions to potential losses often result in individuals making decisions to avoid perceived negative outcomes. Consider a person involved in stock investment is expecting the market to rise and hence is emotionally happy with his financial gains. But suddenly unexpected things happen and the market falls. In such a situation there is a potential loss in his portfolio. This leads to emotional unwellness of the investors, so he carries the loss. There is a kind of a hesitation in his mind to sell the depreciating loss and accept the financial gains that are there in his portfolio.
This loss aversion feeling affects the decision making process which further affects the financial strategies and planning. In the case of stock market the unexpected loss leads to emotional discomfort of the investor. This goes against the rational financial analysis which leads to further losses of the investor.
Cognitive Factors that Shape Decision-Making Processes
Cognitive Load:
This section deals with the effect of cognitive resources usage on decision making efficiency.
Imagine a student preparing for final exam in which he has to cover multiple subjects. The effort required for such preparation is more, as the topics required to study are more. This is cognitive load. It is the mental effort required for processing information.
As the subject matter to study is more, it impacts the decision making process and its efficiency. The important topics, sections, points, paragraphs are more. So more effort is required to juggle between the subjects.
This hinders decision making efficiency. It becomes difficult to be a master of a particular topic a s it is difficult to prioritize such topics. The optimal revision of prior topics can be done, but it difficult to remember, master, or having an intellectual mastery of certain topics.
This is because the cognitive resources are more or the cognitive load is more, which influences complex decision making or multitasking.

Decision Fatigue:
The quality of the decisions start deteriorating as individual faces a higher number of choices or decisions overtime. this phenomenon is studied in cognitive Psychology. Suppose a shopper spends hours at the bustling mall, involving crowd, faces numerous decisions about what to buy, which stores to visit and what items to prioritize.
With the list increasing in number, the shopper experiences decision fatigue. The shopper gets tired, bored physically and mentally, as a result, his ability to make good choices declines because of mental exhaustion. By the end of the day as the energy declines the shopper resorts to impulsive and less optimal choices and decisions.
Because of the accumulation of choices to buy, prioritize thoughout the shopping process there is a decision fatigue in the shopper’s mind about the barrage of choices. Cognitive Psychology extensively studies the insights into how mental fatigue affects decision making processes in various contexts.

Heuristics and Biases:
Academic research has identified numerous cognitive shortcuts and biases that impact decision making process such as availability heuristics and representativeness bias.
Consider a person who is trying to estimate the likelihood of ‘winning a lottery’ which is a rare event. For winning a lottery there is criteria that one should fit into the profile of the lottery. A person may buy a lottery ticket on the basis of the stories heard of the lottery winners.
But it is important to understand the statistical probabilities of a lottery win than hearing to stories of winners. Many a times people have a fixed view or a mindset about something, which influences their decision making. Another example could be investment in a particular stock.
Suppose a person has a good impression about a particular stock. His mind revolves around the successful history of the stock of the the company rather than the present financial statistics and the future prospects being positive or negative about the company. Its negative he can invest in another stock of a company having better financial statistics and better future prospects.
So this heuristics and biases affects the decision making of a person.

Temporal Discounting:
It involves how individuals discount the value of future potential rewards and how decisions are affected by this.
Suppose that an individual has to face choices between getting $100 today or $150 after a month. The fact is that the individual might need money immediately instead of tomorrow. This results in discounting of money reward which he might get later on.
Instant gratification is what is affecting the mind of such people. This influences decision making process as individual navigates tradeoff between immediate benefits, rather than the better rewards which he would get later on. This example shows how temporal discounting in intertemporal choices showcasing the tendency to prioritize present rewards over the future ones in the decision making process.