Why the, test over’s balls varied previously?
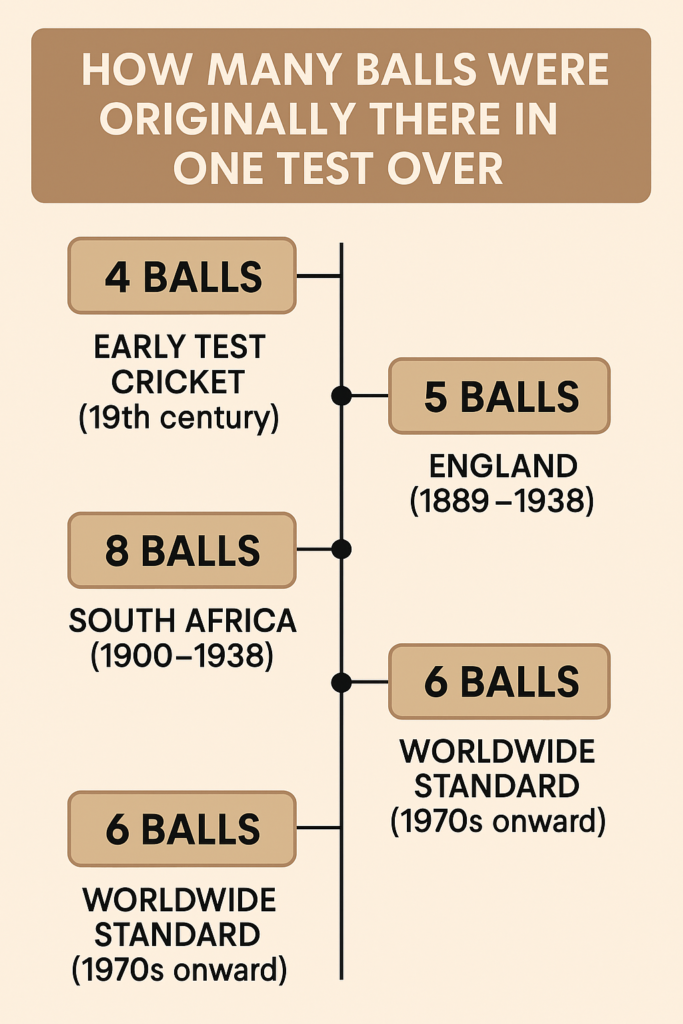
- Originally test cricket over did not always consists of six balls. In fact, overs have historically varied between, four, five, six and even eight balls, depending on the country and era.
- The six-ball over became the only universal standard in 1979-80.
- If you look at the cricketing history, the test cricket game earlier was a bit bowler friendly. Not taking the credit away from the great batters of all time, since the game began.
- The four ball over meant, a bowler would end his over in four balls. So the batter had to face two less balls. This meant a batter had to face a fierce bowler two less deliveries, hence the bowler’s probability of taking wockets was reduced by 2 balls.
- But this meant the stamina and energy of the pace bowlers would be preserved for a longer period of time. six or eight balls in an over, I think, tests patience of cricketers i.e. the batters, as they had to seen through the bowling spells, bowlers, when they encounter good batters, and even fielders, as they have to concentrate for more number of balls.
- The bowlers have to change ends after an over. So four balls mean too little for this. Cricket rules have evolved significantly over time and one of the more fascinating aspects is the number of balls in an over.
- Today we take the six-ball over for granted but historically, Test cricket experimented with different formats before settling on the current standard.
- In the 19th century, when Test cricket began(1877), overs were four balls long in England and Australia. The shorter format meant bowlers had to change ends more frequently and batter faced more bowlers in quick succession.
- Longer overs(like 8 balls) reduced the number of times bowlers had to switch ends, spending up the game. Standardization was needed to ensure consistency across international matches. I think as per todays standards of cricket six balls per over is appropriate for Test and One Day Internationals.
- But for T20’s, the number of balls per over should be reduced to five. The reason for this, I am explaining is the twenty over format is more batting friendly one.
- There are a number of power hitters around the world. But if you consider the bowler’s even good deliveries are away by batters.
- Many say that T20s have less importance of wickets are long partnership takes the game away from the opposition many a times.
- The team who has dominated for most of the time can be loose the game as a result of a high scoring partnership at a good strike rate.
- Many a times a bowler is sent to all parks of the ground bowling 6 balls in a over in death overs as batters are equipped with calculate risks. So bowling six ball in an over becomes more predictable and easy to dominate.
| Country | Balls per Over | Era |
| England | 4 balls | Until 1889 |
| England | 5 balls | Until 1889 |
| England | 6 balls | 1900 onwards |
| Australia | 6 balls | 1900–1973 |
| Australia | 8 balls | 1924–1973 |
| South Africa | 8 balls | 1938–1958 |
| New Zealand | 8 balls | 1968–1979 |
| Pakistan | 8 balls | 1974–1978 |
| Worldwide | 6 balls | Since 1979–80 |
Conclusion
Test cricket originally featured 4-ball overs when it began in the 19th century. Over time, different countries experimented with 5, 6, and even 8-ball formats. England used 5-ball overs until 1938, while South Africa tried 8-ball overs during the same period. Australia adopted 6-ball overs early, and by the 1970s, this became the global standard. The evolution reflects cricket’s journey toward consistency and international alignment.
Timeline based on the Test Cricket Over Length
How many wickets constitute a double hat-trick?
Official account of The Next Test on LinkedIn